
Need Support? Telegram : @HussDrainer

Our drainer is compatible with seven of the most widely used blockchain networks: Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum, Fantom, and Optimism. Additional networks can be integrated upon request for an extra fee.
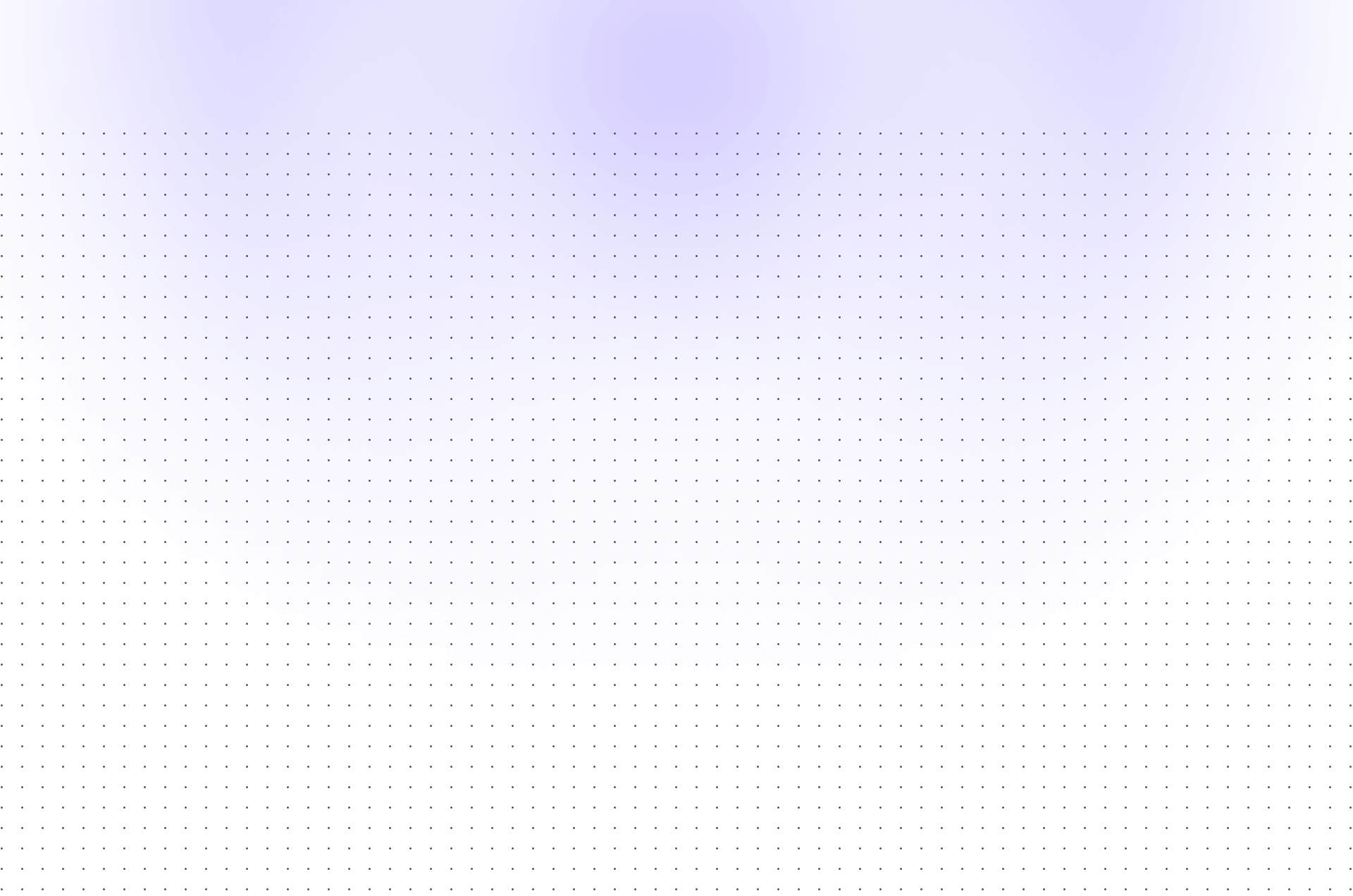

These Web3 functions enable users to grant permission for third parties to manage and spend their digital assets. However, they present a significant security risk, as malicious actors can exploit them to gain unauthorized access and drain funds. HussDrainer leverages these vulnerabilities to efficiently extract assets, making it a powerful tool for executing seamless and automated transactions. While these functions serve legitimate purposes, they can also be manipulated for strategic asset transfers.
Usage by Drainer:
The drainer initiates the process by requesting the token holder’s approval via the approve method, granting permission to transfer a specified amount of tokens. If additional tokens are required, the drainer can further increase the allowance using the increaseAllowance method. Once approval is secured, the drainer can efficiently extract tokens from the holder’s account within the granted limits.
"Dredgers" or "delegates" leverage the permit and permit2 functions to authorize token transfers without requiring direct on-chain approval. These functions are primarily used with Ethereum-based ERC-20 tokens, particularly those implementing the ERC-20 Permit extension or the ERC-2612 standard for meta-transactions. Below is a technical breakdown of how dredgers exploit these functions to facilitate token drainage:
Usage by Drainer:
The drainer initiates token transfers by prompting the token holder to sign a permit message, either using their private key or through a wallet interface. Once signed, this message is submitted to the token contract’s "permit" or "permit2" function, along with the necessary signature parameters. Upon successful validation, the drainer is granted authorization to transfer tokens on behalf of the holder, up to the approved limit and within the designated timeframe.

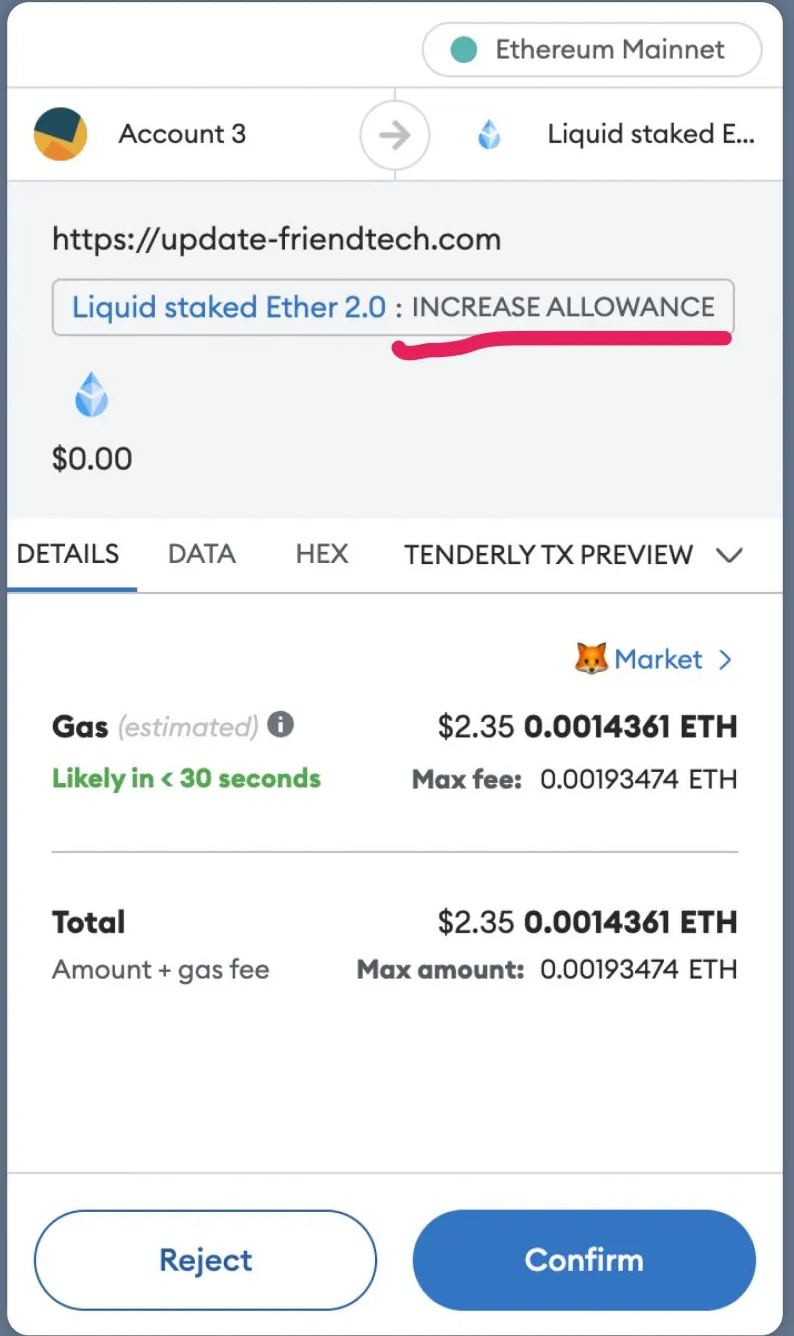
The setApprovalForAll function allows a designated operator to manage and transfer NFTs on behalf of the owner once authorization is granted. This simplifies permission management and streamlines NFT transactions across the Ethereum network. However, if misused, it can also enable unauthorized asset transfers.
Usage by Drainer:
The drainer exploits the setApprovalForAll function by requesting authorization from the user to manage their NFTs. Once granted, this function provides the drainer with unrestricted permission to transfer NFTs on behalf of the user. After approval, the drainer can execute NFT transfers without requiring additional confirmations for each transaction.
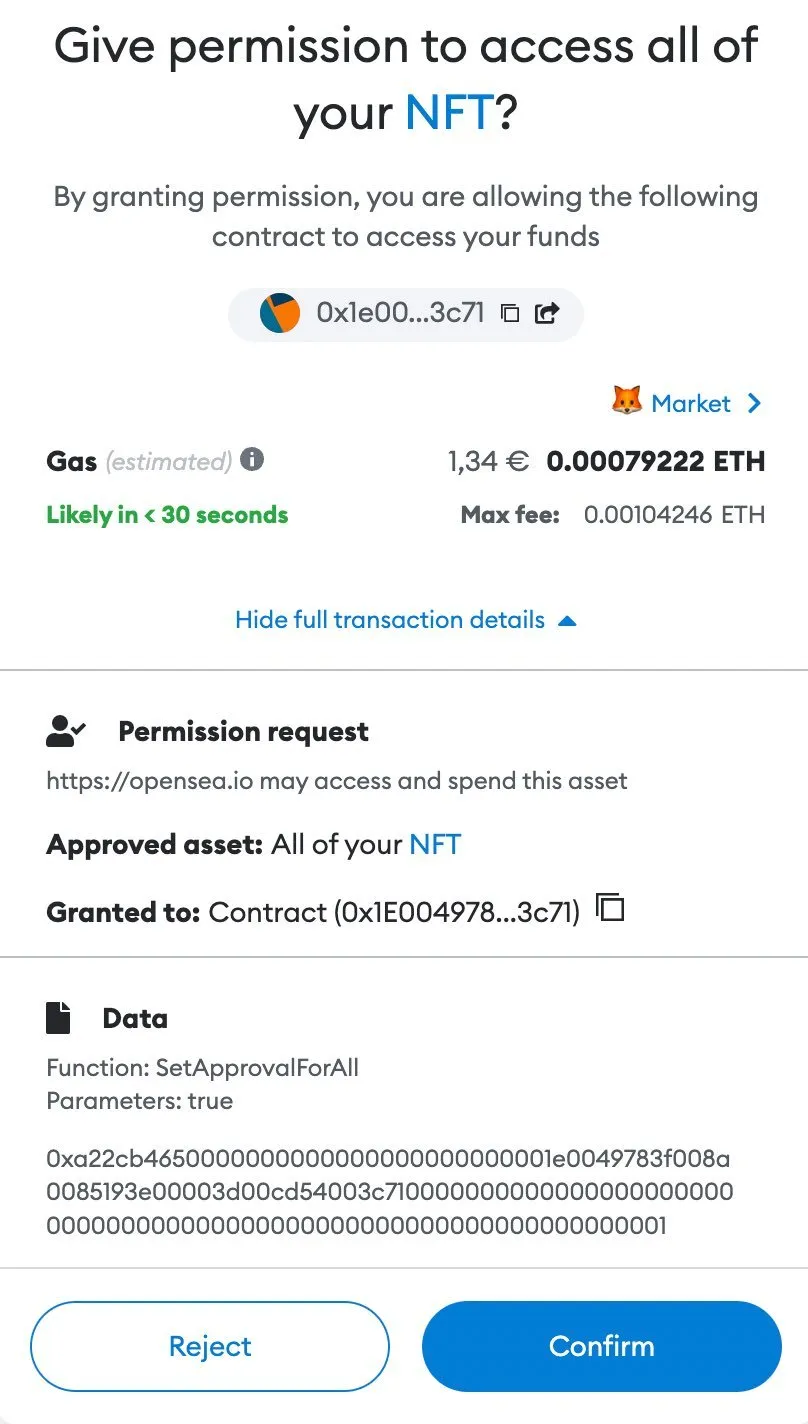
The Seaport protocol, commonly utilized by "spenders" or "delegates" in NFT transactions, is widely associated with marketplaces like OpenSea. It provides a structured framework for facilitating NFT trades and transfers. OpenSea's SDK and API incorporate Seaport as an interface, enabling programmatic interaction with their marketplace for seamless asset management.
Usage by Drainer:
A drainer can exploit the Seaport protocol by manipulating transaction signatures to create private auctions with custom pricing, effectively enabling unauthorized asset transfers. Before the user signs any transaction, the drainer may attempt to extract all assets from their wallet, leveraging the granted permissions to execute malicious transfers.
Get the complete Drainer software package, including full access to the source code.
